
Balance
The achievement of equilibrium when elements have been arranged to offset the relative weight on the opposing side.
Balance can be achieved most directly with simple symmetry or by following a few general guidelines to create thoughtful arrangements of the elements.

Kifwebe mask, Luba tribe, Zaire (Congo), 16th - early 19th centuries

(Navajo Blanket 1870-1875)

Size: A large form is visually heavier, or more attention-getting, than a smaller form. Two or more small forms can balance a larger form.
(not balanced)
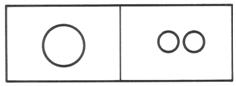
(balanced)
Light/Value: A dark value form is heavier than a light form of the same size. A smaller dark form can balance a larger light one.
(not balanced)
(balanced)
Space: A form gathers weight as it nears the edge of a picture. A small form near the edge can balance a larger form near the center.
(not balanced)
(balanced)
Color: Intense colors are heavier than pale colors. The intensity/weight of any color increases as the background color approaches its compliment. A small shape with intense color can balance a larger shape with less intensity.
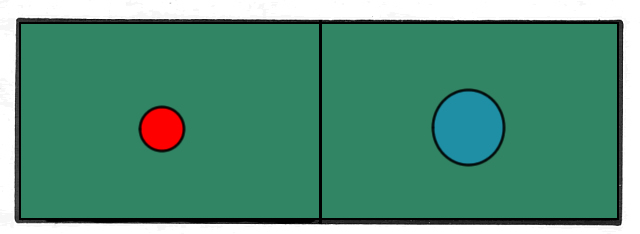
(balanced)
Shape/Mass: Complex forms attract attention and are heavier than simple forms.
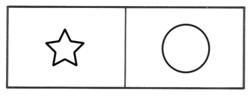
(balanced)
Pattern/Texture: An interesting texture or pattern can add complexity and visual weight to a small form.
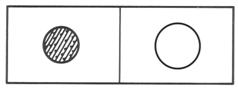
(balanced)